Pain and touch sensations require Schwann cells
The skin contains a vast number of sensory receptor endings that detect touch, heat and cold, but also potential dangers such as harmful mechanical and chemical stimuli. These sensory celle then send a corresponding signal to the spinal cord and brain. Scientists had previously thought that sensory neurons alone were responsible for this task. However, it turns out that Schwann cells also play a vital role, as the groups of Professor Gary Lewin and Professor James Poulet from the Max Delbrück Center, along with an international research team now report in the journal “Nature Communications.”
Schwann cells are known to act as an insulating layer around nerve fibers. They protect and provide nutrients to neurons. Yet new research has shown that specific types of Schwann cells are also actively involved in detecting sensory stimuli. These Schwann cells form a network-like structure just a few micrometers below the epidermis, and are connected to the free nerve endings of sensory receptors that detect mechanical pressure. “We were surprised at the extent to which the Schwann cells participate in stimulus detection,” says Gary Lewin, head of the Molecular Physiology of Somatic Sensation Lab at the Max Delbrück Center.
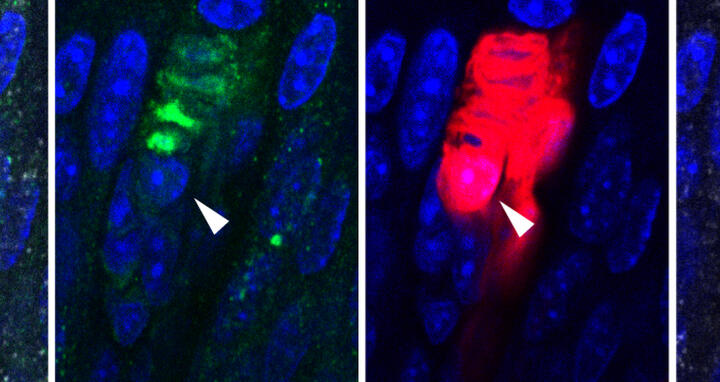
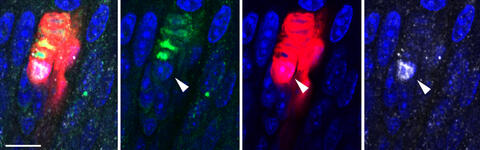
Sensory Schwann cells positive for SOX10 shown in red, sensory-ending within the Meissner corpuscle in green, SOX2-postive cell at the base of the Meissner corpuscle shown in silver.
The first indications of the importance of Schwann cells in pain perception (nociception) came from earlier studies by Lewin’s Swedish collaborators. This prompted Julia Ojeda-Alonso from the Lewin lab and Poulet’s lab to team up with international colleagues like Dr Laura Calvo-Enrique from the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm – in order to get to the bottom of the matter. Using a technique called optogenetics, the researchers bred mice in which they were able to switch different types of Schwann cells on and off with different colors of light.
Without Schwann cells, the mice could not sense vibrations
All it took to convey pain sensations to the brain was to activate the Schwann cells with a light stimulus. It was not necessary to stimulate the actual nociceptors. When the Schwann cells were blocked, the transmission of stimuli by nociceptors was reduced by at least half. “We assume that technical limitations prevented us from being able to fully map the role of Schwann cells and that in some cases they actually perform most of the stimulus detection ,” says Lewin.
The team next ran experiments with tactile stimuli. They focused on the Meissner corpuscles, which are vibration receptors in the skin that are closely associated with Schwann cells. The team led by James Poulet, who heads the Neural Circuits and Behavior Lab at the Max Delbrück Center, trained the mice to sense tiny vibrations with their forepaw and to report detection of these stimuli. “When the Schwann cells were switched off, it was much more difficult for mice to do this,” explains Poulet. After the optogenetic blockade was removed, their ability to sense tiny skin vibrations returned.
New approaches for pain therapy
The researchers showed that the Schwann cells primarily influence the transmission of mechanical stimuli, but not heat or cold stimuli. “It may be that polymodal nociceptors, which react to mechanical, thermal and chemical stimuli, only function properly with the help of Schwann cells,” says Lewin.
The results open new avenues for understanding and treating pain and impaired touch perception. “The Schwann cells just below the surface of the skin are easily accessible to therapeutic agents,” says Lewin. “This makes them an attractive target for tackling the problem right at the root.”
Text: Stefanie Reinberger
Further information
Literature
Julia Ojeda-Alonso, Laura Calvo-Enrique, Ricardo Paricio-Montesinos et al. (2024): “Sensory Schwann cells set perceptual thresholds for touch and selectively regulate mechanical nociception.” Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44845-8
Picture to download
Sensory Schwann cells positive for SOX10 shown in red, sensory-ending within the Meissner corpuscle in green, SOX2-postive cell at the base of the Meissner corpuscle shown in silver. Photo: Lewin Lab, Max Delbrück Center
Contacts
Prof. Gary Lewin
Head of the Molecular Physiology of Somatic Sensation lab
Max Delbrück Center
+49 30 9406-2270 (office)
glewin@mdc-berlin.de
Jana Schlütter
Editor, Communications
Max Delbrück Center
+49 30 9406-2121
jana.schluetter@mdc-berlin.de or presse@mdc-berlin.de
- Max Delbrück Center
The Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (Max Delbrück Center) is one of the world’s leading biomedical research institutions. Max Delbrück, a Berlin native, was a Nobel laureate and one of the founders of molecular biology. At the locations in Berlin-Buch and Mitte, researchers from some 70 countries study human biology – investigating the foundations of life from its most elementary building blocks to systems-wide mechanisms. By understanding what regulates or disrupts the dynamic equilibrium of a cell, an organ, or the entire body, we can prevent diseases, diagnose them earlier, and stop their progression with tailored therapies. Patients should be able to benefit as soon as possible from basic research discoveries. This is why the Max Delbrück Center supports spin-off creation and participates in collaborative networks. It works in close partnership with Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin in the jointly-run Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), the Berlin Institute of Health (BIH) at Charité, and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK). Founded in 1992, the Max Delbrück Center today employs 1,800 people and is 90 percent funded by the German federal government and 10 percent by the State of Berlin.